Type of Taxes (Income Tax Act,1961)
September 18, 2019
“Taxes are paid and nations are made”. However not many are aware that government asks to pay taxes in different manners. Taxes are financial charges imposed on an individual or a company by central government or state government. It is important to understand the different types of taxes that are applicable in India.

Types of direct tax in India
Direct taxes are obligatory and have to be directly paid to the Government of India. There has been a gradual and steady increase in the direct tax collections in the recent years in India. The increase in collection of direct taxes is indeed a positive sign, showing more people are earning taxable incomes. Some of the direct taxes made obligatory by Government of India are:
Income Tax
If money is earned then tax has to be paid – if it crosses a particular slab of income received. Income tax returns have to be filed in different forms for different types of businesses and individuals. There are different ITR forms available for salaried, self employed, partnership firms and more. Checkout this article for more information about the different types of ITR forms.
Capital Gains Tax
The profit you make on sale of a property attracts capital gains tax. For e.g If a property worth 30 lakhs is sold for an amount of 80 lakhs then capital gains tax is applicable on the 50 lakhs difference amount including the 3% education cess, 20% on the long terms capital gains tax and inflation index of the year the property was purchased plus and the inflation index of the year the property was sold.

Securities Transaction Tax
This type of tax is applicable when customer purchases or sells equity shares, derivative instruments, equity oriented mutual funds. This tax cannot be avoided as it is added during the transaction itself. MoSt often this tax goes unnoticed because only a small amount is what gets deducted.
Fringe Benefit Tax or Perquisite Tax
Fringe benefit tax was abolished in the year 2009. It used to be applicable on non-monetary benefits offered to employees like cars, club memberships etc. Presently all of these benefits are taxable under perquisite tax.
Corporate Tax
If a corporate organisation (Eg: Private Limited Company or Limited Company) is operating in India then corporate taxes is applicable on the income generated by the company. Unlike, individuals taxation, there are no slabs and income tax is applicable on the total taxable profits of the company.
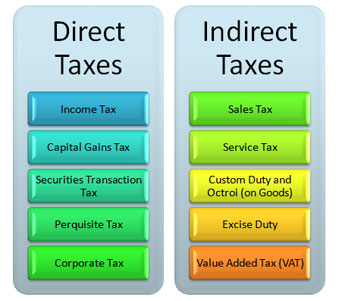
Types of indirect tax in India
Indirect taxes are levied on individuals but paid by another individual or company. For e.g. value added tax, sales tax etc are all indirect taxes. Wherein, a customer makes service tax payment on a restaurant bill, its collected by the restaurant and remitted to the Government.
Service Tax
Most of the services offered in businesses such as software companies, restaurant, travel agents, etc charge service tax for offering paid services. Service provided by businesses such as travel agents, tour operators, health center, banking and financial services and more are liable to pay service tax. The current rate of service tax in India is 14%
Value Added Tax (VAT)
VAT or Value Added Tax is an important tax for State government, as its a major source of revenue for State Governments. VAT is applicable on the sale of goods and products. Every state has their respective Sales Tax or VAT Act. The VAT rates also differ based on the item in India from one state to another.
Custom Duty
Goods imported into India from a foreign country will attract custom duty. Customs duty is collected at the port of entry by the Customs Department.
Central Excise
Central Excise Duty is a form of Indirect Taxation levied through the Central Excise Act, 1944. The Central Excise Duty is levied on Goods and Products, which are manufactured or produced in India. Excise duty is levied when the goods are manufactured or produced in India and is payable when the goods are removed from the manufacturing premises.

